Water rich in dissolved minerals, particularly calcium and magnesium, is referred to as hard water. The minerals are not harmful to human health, but they can create various problems in the home.
When hard water is heated, it generates calcium carbonate or scale, the unattractive mineral deposits that build up in your pipes and appliances, causing the greatest problems.

There are several solutions for bringing soft water into your house without having to install a water softener. Hard water can be softened by various methods, including boiling it before using it, adding chemicals, or using filters.
Each of these procedures will remove the magnesium and calcium minerals that cause hardness in the water and reduce the impact of pollutants such as chlorine and lead in the water supply.
Recognizing hard water

- The flow of water is reduced: You may notice a drop in water pressure from your taps due to limescale accumulation in your pipes.
- The energy cost is greater than usual: Your energy expenses may rise due to your appliances having to work harder owing to limescale.
- Hair and dry skin: Minerals can collect on your scalp, making your hair dry and brittle. Mineral residue can irritate your skin as it might irritate your eyes.
- More soap is required for household chores: Hard minerals substantially impact soap and shampoo, reducing soap production and causing difficult-to-remove soap scum. Because the minerals inhibit water and detergent from foaming, your clothes may lose color and clean less effectively.
- Hardness is shown through water tests: DIY test kits are easily available online for rural residents. Follow the instructions in this article to find out how hard your water is.
- Spots, streaks, and a foggy film appear on your dishes when they come out of the dishwasher.
- If you see chalky deposits on the inside of your faucets or brown stains on your toilet, it’s time to call a professional.
Water softening without a water softener.
The flavor of hard water is a bit unpleasant, but that isn’t the major problem with it. When used in the kitchen, it can cause a white film of salt to form on your utensils, essentially corroding them.
It can clog your kitchen sink and damage everything in the worst-case scenario. Boiling your kitchen water is the greatest method to soften it.
Boiling causes the salts in the water to thicken, and they will settle at the bottom of the container after a while. Later, you may scoop off the water or pour it into another pot, leaving the deposits behind.
How do you go about doing it?
- Take a large saucepan and thoroughly clean it.
- Fill it with water and bring it to a boil.
- Remove the saucepan from the heat and set it aside for a few hours.
- Pour the upper layer of clean softened water into a separate container and discard the accumulated salt deposits.
- Use this water to clean and wash around your kitchen; you won’t have to worry about blocked drains or unsightly sinks anymore.
DIY hard water treatment
- When making coffee in the morning, use bottled water instead of tap water.
- Install a showerhead that has a built-in filter.
- After bathing, apply a decent moisturizer to prevent your skin from drying out due to rough water.
- Wash your hair with bottled water or add apple cider vinegar or lemon juice to your hair care routine.
- Turn off your washing machine’s hot water valve and only wash your garments in cold water.
- Set your dishwasher at a low drying temperature.
- Vinegar should be used to scrub hard water stains. Remove stains, white spots on cloth, and mineral build-up on the appliance with apple cider or white vinegar.
- Regularly clean the debris within your pipes and appliances. If you are familiar with plumbing, this might be a do-it-yourself effort. Otherwise, get a professional. It will extend the life of your equipment.
More water softening methods
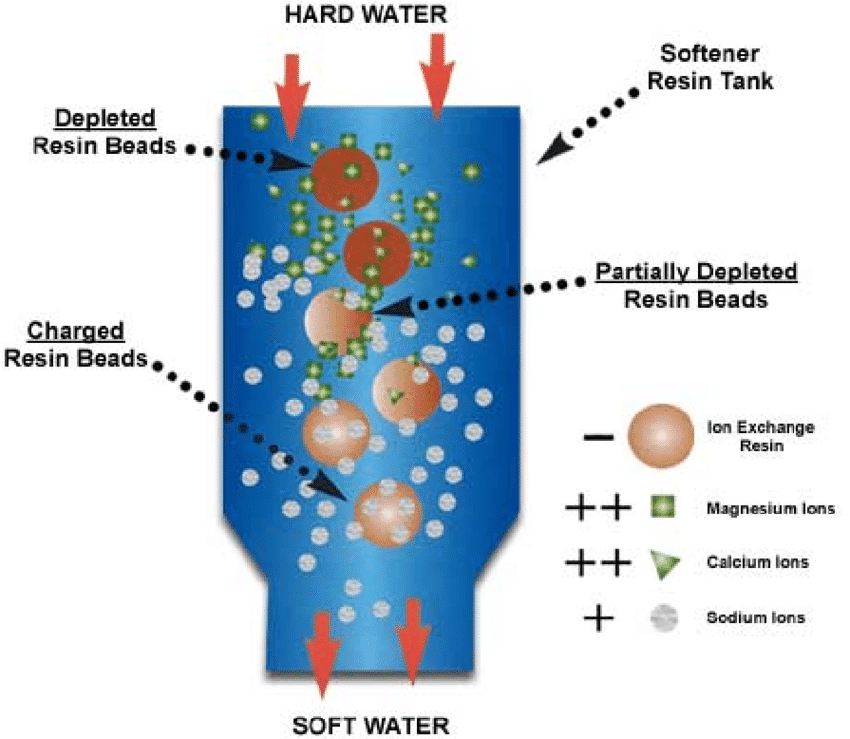
Ion exchange

The most common type of water softener used for residential home water supply is salt-based ion-exchange water softeners. They function by removing calcium and magnesium ions from the water and replacing them with sodium or potassium ions that coat the resin beads in the ion-exchange tank, causing the water to become less hard.
About once a week, the system must be regenerated to replenish the water softening ions that have been depleted and wash out the hardness ions that have replaced them. Water softeners that use ion exchange technology may also remove dissolved ferrous iron from the water supply.
Nucleation Assisted Crystallization (NAC) or Template Assisted Crystallization (TAC)
This type of water conditioning is still relatively new in commercial applications but is already available on a home scale. The method has been shown to minimize lime-scale development in hard water by over 96% in controlled testing conducted by the University of Arizona.
The procedure works on the idea that microscopic ceramic polymer beads in an active environment include sites or templates that function as anchors for calcium and magnesium hardness ions to aggregate into nano-crystal clusters.
These clusters break away from the beads and are carried back into the water flow once they have grown to a certain size but are still minuscule. TAC is effective for hardness up to 25gpg at a flow rate of 7gpm; however, it is rated for significantly greater hardness levels, up to 75gpg.
Reverse Osmosis (RO)

Reverse osmosis is a method of filtering water by pushing it through a succession of extremely tiny filters under pressure to remove all pollutants down to the molecular level.
All chemicals and organic dissolved particles, including hardness-causing calcium and magnesium ions, have been eliminated, yielding a product identical to distilled water. As a result, a Reverse Osmosis filter system might be classified as a type of water softener.
Chelation system
Chelation is the process of conditioning hardness-causing ions in water so that they do not react with other chemicals in the water to produce lime-scale. This method has been used for decades to cleanse water in business applications such as factories, laundries, and restaurants, but it is now available for home use.
The benefit is that calcium and magnesium ions stay in the conditioned water and can give health advantages when ingested. The sodium level of the water does not rise for individuals on low-sodium diets for health reasons.
Is there a way to avoid using a water softener?
A salt-free water softener, an alternative to sodium or potassium-based water softening and frequently wrongly referred to as softening, is another choice for a water softener. If you’re fed up buying salt for your salt-based water softener, a water conditioner might be the answer.
They negate the detrimental effects of “hardness” particles by encapsulating them in calcium carbonate crystals and altering their molecular composition, preventing them from adhering to appliances and plumbing pipes.
Final thoughts
While all of the alternatives to a water softener may work momentarily, they are only band-aid solutions that do not address the underlying issue. If you own your house and are searching for a long-term solution, using an ion exchange water softener is the only method to eliminate hard water in your home.
In the long run, we strongly advise you to investigate and consider installing a whole-house water softener.

Jay
Jay is a health and wellness enthusiast with expertise in water quality and nutrition. As a knowledgeable advocate for holistic well-being, Jay successfully manages Type 2 Diabetes through informed lifestyle choices. Committed to sharing reliable and authoritative insights, Jay combines firsthand experience with a passion for enhancing health."

