Are you looking for an easy way to measure the quality of your water? Total dissolved solids (TDS) is a great way to get an overview of the health of your water. In this blog post, we’ll explain what TDS is and why it’s important. We’ll also give you some tips on how to test and reduce TDS in your home.
Table Of Contents
−- What is TDS?
- What Is Measured by TDS?
- Where does TDS come from?
- How is TDS measured?
- Types of dissolved solids
- What are the benefits of taking a TDS reading?
- How TDS level affects your water:
- What you cannot measure with a TDS:
- Ways to lower TDS level
- How Can Low TDS Levels Be Increased?
- What Is the Ideal Level of TDS for Drinking Water?
- Conclusion
What is TDS?
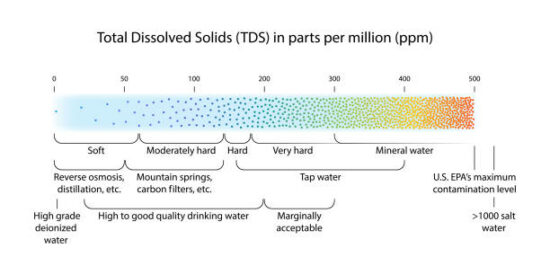
Total dissolved solids (TDS) measure the total amount of organic and inorganic substances in drinking water. This includes minerals, salts, metals, and ions. TDS levels can range from 0 to over 10,000 parts per million (ppm), with anything over 500 ppm considered high. High TDS levels can lead to unpleasant tastes and odors in drinking water and health risks.
What Is Measured by TDS?
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) measure the combined content of all inorganic and organic substances in a liquid. It is measured as a volume of water with the unit milligrams per liter (mg/L), otherwise known as parts per million (ppm).
TDS can be measured in the field using an electronic pen or device, which measures the conductivity of the water. TDS is an important measure of water quality, as it indicates the number of minerals in the water.
High TDS levels can indicate pollution or contamination and should be monitored closely. Low levels may also cause concern, indicating a lack of necessary minerals for healthy drinking water.
Where does TDS come from?
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) come from a variety of sources, both natural and artificial. Natural sources of these substances include springs, lakes, rivers, plants, and other organic matter. In addition, materials may leach into water from sewage, water treatment chemicals, agricultural runoff, or industrial wastewater.
This means that TDS levels can vary based on the local environment and the type of water source. It is important to understand the source of your water to determine its quality and safety. Fortunately, there are ways to monitor and reduce TDS levels to maintain safe drinking water.
Why is solid dissolved?
Rainwater can dissolve minerals in the rocks and soil it runs over and through. Different concentrations of these minerals persist in the water as it dissolves them. This is a completely natural process that slightly increases the pH of the water, which is one of the factors responsible for giving it that “just right” flavor. Calcium, magnesium, and salt are the most prevalent minerals in water.
How is TDS measured?
Total dissolved solids (TDS) can be measured in the field using an electronic pen. These devices measure the conductivity of the water, which is the ability of a liquid to conduct an electrical current. The TDS value is then calculated by measuring the electrical conductivity of the water sample.
TDS can also be measured in a laboratory using various methods such as evaporation, filtration, and precipitation. It is important to note that different methods may lead to different results, so a laboratory test should always be done for accuracy. It is important to ensure that any equipment used for TDS measurement is calibrated properly to get accurate results.
How do you measure TDS?
The easiest approach to determine the total dissolved solids in your water is to use a TDS meter.
If a TDS meter reads 100 ppm, it indicates that out of every million particles, only 100 are dissolved ions, and the remaining 999,900 are water molecules. A TDS of this magnitude is regarded to be quite low.
However, the most crucial data about your water quality is not provided by a TDS meter: the types of TDS present. Therefore, it is advisable to use either a home water test kit or a laboratory water analysis to determine the specific TDS forms in your water.
How to calculate TDS
Here is the formula for computing TDS
%Rejection= [(Tap TDS-RO TDS)/ Tap TDS] x 100
What is the unit of measure in a TDS?
Milligrams per liter (mg/L), sometimes known as parts per million, is the unit of measurement for total dissolved solids (TDS) in water (ppm). The highest acceptable TDS level for drinking water is 500 ppm. TDS levels above 1000 ppm are considered hazardous. Over 2000 ppm can compromise the efficiency of a filtration system when trying to remove TDS.
How does a TDS meter work?
Total dissolved solids in a solution, often water, can be read off using a portable TDS meter. A TDS meter examines the conductivity of a solution to determine its TDS because dissolved ionized solids, such as salts and minerals, enhance a solution’s conductivity.
TDS meters are also known as TDS testers and PPM (parts per million) testers; however, these names are merely marketing ploys to differentiate between the two types of devices. A simple TDS meter may determine the total dissolved solids in a solution. In contrast, a more complex model may be able to test for salinity, temperature, and more.
Types of dissolved solids
The following is a list of typical TDS that could be found in your water supply.
- Aluminum
- Arsenic
- Bicarbonates
- Calcium
- Chloride
- Chlorine
- Copper
- Fluoride
- Herbicides
- Iron
- Lead
- Magnesium
- Pesticides
- Potassium
- Sodium
- Sulfates
- Zinc
What are the benefits of taking a TDS reading?
Dissolved solids, most often minerals, are abundant when the TDS reading is high. Scale accumulation in your plumbing and appliances due to these minerals in your water can reduce their useful life and shorten their useful lifespan.
How TDS level affects your water:
The TDS level of your water will tell you if you need a salt-free water softener or a water softener to deal with hard water. Without wasting salt or water, salt-free water softeners provide numerous benefits, including pipe and fixture preservation, reduced staining on dishes and shower doors, prolonged brilliance of clean laundry, and more.
Do not confuse a Salt-Free water softener with a water filter. As counterintuitive as it may seem, a water filter’s ultimate purpose is not to purge the water of all solids.
It has a distinct odor and taste
High TDS (total dissolved solids) in municipal tap water can give it an off flavor and odor. In general, water tastes worse as its total dissolved solids concentration rises.
It changes your food’s flavor
Water with a high total dissolved solids (TDS) concentration might alter food flavor when cooking, but it won’t harm you if the TDS is below 1000 ppm. Pasta, for instance, may take on an unpleasant flavor from the boiling water if your water supply contains a lot of chlorine. A carbon filter is the best option to eliminate water’s chlorine taste and odor.
It can be harmful to your health
Drinking water with a high TDS may not harm your health in and of itself, but it may include toxic metals like lead or copper. Some toxins, like lead, can harm your brain and nervous system, while others, like copper, can make you sick. A reverse osmosis system or a water distiller is suggested to remove pollutants like lead and mercury from water.
It can damage your plumbing and appliances
Hard water is water with high quantities of dissolved calcium and magnesium, which can cause high total dissolved solids. Scale buildup, caused by the dissolution of calcium and magnesium salts, is expensive to fix and shortens the lifespan of your plumbing and appliances. Scale formation can be avoided with a water softener, which removes hard minerals like calcium and magnesium from the water.
It can affect the cleanliness of your sink, dishes, and laundry
Total dissolved solids may be to blame for the buildup in your sinks, the persistence of water spots on your dishes, and the fading of your laundry. A water softener or other filtration device could reduce TDS and improve cleaning performance.
What you cannot measure with a TDS:
Knowing what a TDS meter does not test for before making a purchase is vital. Some things that can’t be measured with a TDS meter include the following:
Contaminants
A TDS meter can tell you how many parts per million (PPM) of total dissolved solids are in your water, but it can’t identify the specific substances. Hence, what is polluting the water can’t be seen on a TDS meter.
Compounds and metals
Because it can only measure dissolved solids, a TDS meter might not pick up on pollutants, including lead, medicines, certain pesticides, and chromium-6.
Water health
You shouldn’t assume that since your water has a high TDS level that it’s unhealthy to drink. Your water’s high TDS could be due to beneficial dissolved minerals, including calcium, magnesium, and potassium. There may be no dangerous pollutants in the water even though the TDS is high. Bottled water won’t cut if you want low TDS unless treated with RO filtration.
Efficiency of filtration
A TDS meter should not be used to test the effectiveness of a typical water filter. Only filters specifically intended to reduce TDS from water, such as reverse osmosis filters, can measure their efficacy by a TDS meter. Additional filters may have a minimal effect on TDS, but they probably won’t have much of an effect on your reading otherwise.
Ways to lower TDS level

If the TDS level in the water is 500 ppm or greater, several water treatment systems can effectively reduce or eliminate the TDS. The type of TDS in your water will determine which filter system will be most effective. Here are some ways you can employ to reduce TDS levels.
Reverse osmosis
Regarding filtering out impurities, reverse osmosis (RO) systems are among the most effective. This method uses pressure to force unfiltered water through a semipermeable membrane. The membrane’s microscopic pores are designed to keep out dirty water while letting pure water pass through.
Deionization
Deionization systems use resins that regulate ionic charge to eliminate TDS in water via ion exchange. Ions from water molecules are used instead of charged ions from TDS. High-purity filters are another common name for deionization cartridges because they generate extremely clear water.
Distillation
Distillation is a process used to purify water, similar to how water is naturally cleansed in the atmosphere through evaporation. Water distillers remove total dissolved solids and other impurities because they do not evaporate into steam as water does. Water is safe to drink once it has melted back into a liquid.
How Can Low TDS Levels Be Increased?
Low TDS levels can be increased by adding mineral salts such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium to the water. This is often done through a water softener, which removes existing minerals from the water and replaces them with new minerals.
A water softener effectively increases TDS levels, as it allows for a precise amount of minerals to be added. Following the manufacturer’s instructions when using a water softener is important, as too much or too little mineral can hurt the water.
Additionally, various filtering methods can increase TDS levels in drinking water. These include reverse osmosis systems, activated carbon filters, and ion exchange resins.
What Is the Ideal Level of TDS for Drinking Water?
The ideal level of Total Dissolved Solids for drinking water is highly debated, as different organizations have different standards. The Water Systems Council recommends a TDS level of 500 parts per million (ppm) or less, while the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends 300 ppm. However, the normal TDS level ranges from 50 ppm to 1,000 ppm, according to the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). Therefore, it is important to consider the source and quality of drinking water when determining the ideal TDS levels for consumption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, total dissolved solids (TDS) are an important measure of the concentration of all inorganic and organic elements dissolved in water. TDS can come from various sources, such as minerals, salts, metals, cations, or anions dissolved in water.
It is important to measure the TDS level to determine how mineralized the water is and avoid potential health risks. High TDS levels can be reduced by using a reverse osmosis filter or distillation system, while low TDS levels can be increased by adding minerals such as calcium and magnesium.
The ideal level of TDS for drinking water is generally below 500 ppm, although this may vary depending on your local regulations and standards. With these tips in mind, you should be able to make sure your drinking water has the right concentration of total dissolved solids for your health and well-being.

Jay
Jay is a health and wellness enthusiast with expertise in water quality and nutrition. As a knowledgeable advocate for holistic well-being, Jay successfully manages Type 2 Diabetes through informed lifestyle choices. Committed to sharing reliable and authoritative insights, Jay combines firsthand experience with a passion for enhancing health."


