Are you concerned about the environmental effects of fracking? Are you wondering how it’s impacting water quality? If so, then this blog post is for you. We’ll explore the science behind fracking and its potential impacts on local water sources.
What is Fracking?
Fracking, also known as hydraulic fracturing, is used to maximize the extraction of natural gas and other natural products in geothermal wells by many companies.

Fracking is extracting oil and gas from underground shale formations using high-pressure water, sand, and chemicals injections. It is a relatively new method of extracting resources and is becoming increasingly popular due to its cost-effectiveness and potential to unlock vast energy stores.
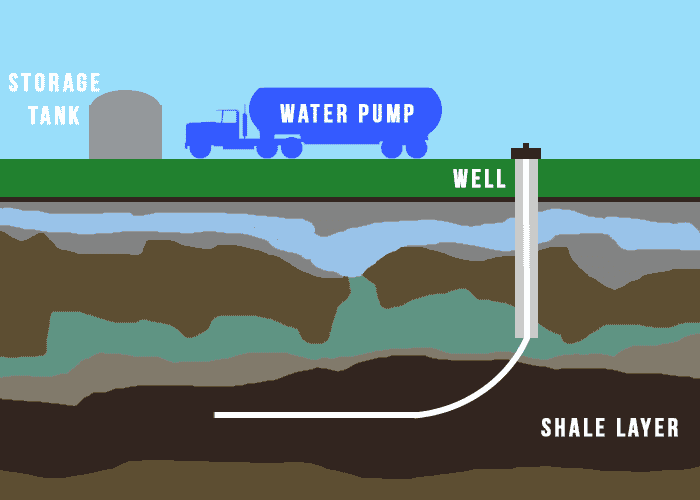
Sources of Contamination from Fracking
The sources of contamination from fracking can vary, but the most common are related to chemicals and wastewater. Chemicals used in fracking, such as acids and surfactants, can leach into the water table and cause contamination.
Wastewater produced after water injection deep into the rock during fracking can contain industrial chemicals and leached compounds, which can also cause contamination. In addition, methane can escape from wells during the fracking process, resulting in methane contamination of groundwater.
All these sources of contamination can seriously impact water quality, and it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with fracking.
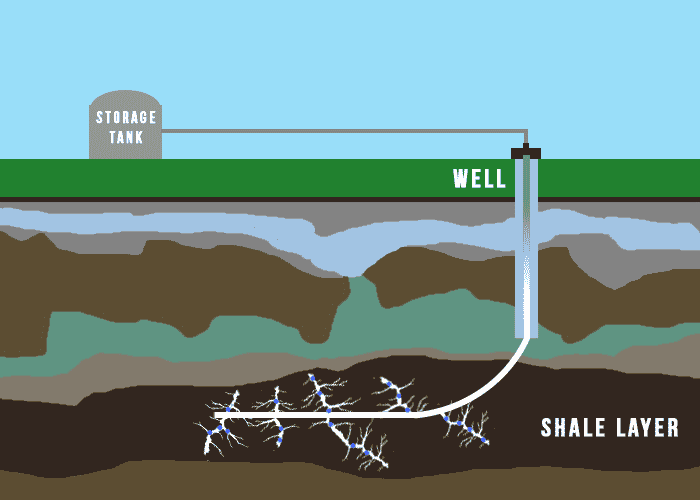
Fracking is purposely used to boost the rate at which natural products, e.g., water, petroleum, and natural gases, can be recovered from subterranean porous reservoirs. It also stimulates underground wells and measures stress on the earth.
Chemical Impacts of Fracking on Water Quality
Regarding fracking, the potential chemical impacts on water quality are a major concern. Chemicals used in fracking fluid, such as methanol, hydrochloric acid, and isopropanol, can contaminate surface and groundwater. These chemicals can leach from the well and seep into nearby streams, rivers, and groundwater.
In addition, wastewater produced from the fracking process may contain various industrial chemicals, solvents, and salts that are potentially hazardous to humans and wildlife. Research has shown that these chemicals can reduce drinking water quality and lead to long-term health effects. Therefore, it is essential that proper regulation and monitoring of fracking operations is in place to ensure that water quality is not affected by fracking.
Some companies dispose of wastewater like hydrocarbon waste by injecting them deep underground. Others use fracking to generate electricity, induce rock cave-ins for mines, and geological sequestration of carbon dioxide.
Physical Impacts of Fracking on Water Quality
Fracking operations can also cause physical changes to the composition of water. The process of hydraulic fracturing requires large amounts of water, which can deplete water supplies in the area of the well.
In addition, the hazardous chemicals used in the fracking process can cause changes in the pH level of the water. This can reduce the water quality and make it unsuitable for drinking, irrigation, or other uses.
Furthermore, the wastewater produced by fracking operations can also contain large amounts of suspended solids, which can contribute to sediment buildup and restrict the flow of rivers and streams. These physical changes can impact the environment and the region’s water quality.
Though necessary, these practices bring hazardous effects on humans and the environment. Fracking has been associated with causing micro-earthquakes. Injecting wastewater underground has been associated with earthquakes of a magnitude of 5.0 on the Richter Scale in the US.
Methane Contamination from Fracking
Methane contamination is another potential concern regarding fracking and water quality. Methane is a naturally occurring gas released during fracking and can enter aquifers and other water sources.
Methane contamination has been linked to an increased risk of explosion and can also contribute to climate change. The Duke University study referenced earlier found methane contamination was more common in fracking areas. This is concerning, as methane is highly flammable and can be fatal if inhaled in large quantities.
As a result, regulators must ensure proper safety measures are in place to protect water sources from methane contamination. Additionally, monitoring water sources in areas where fracking has taken place is necessary to ensure that methane levels remain safe.
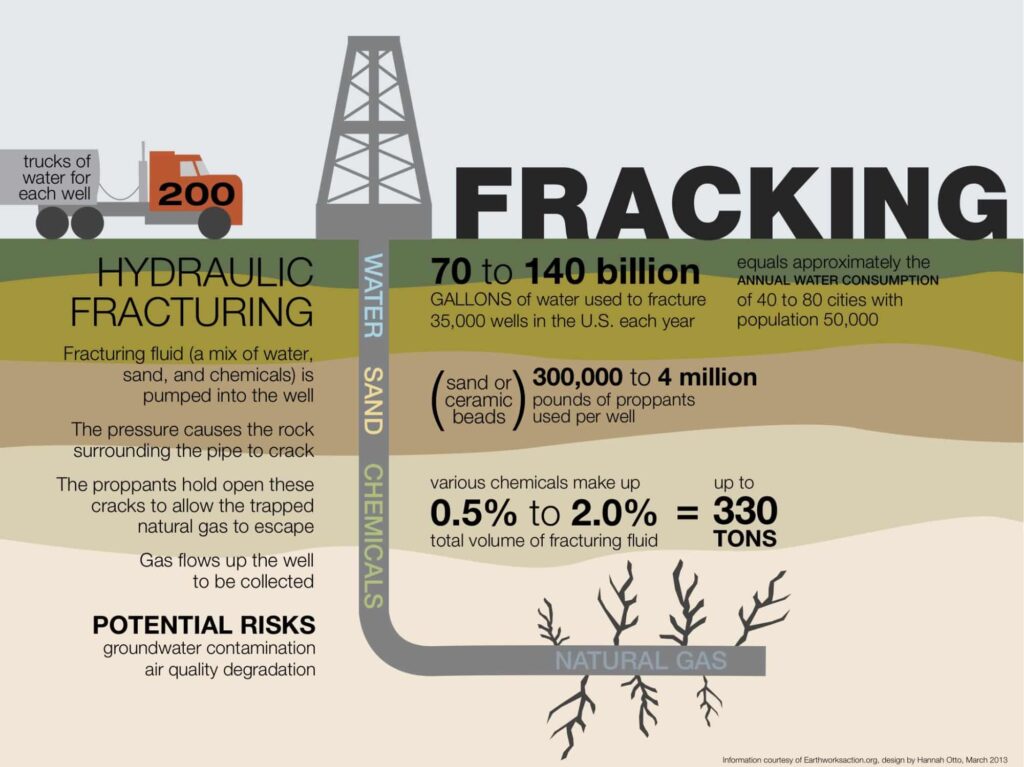
Regulation and Monitoring of Fracking Operations
The practice of hydrofracking is highly regulated, and all operations must adhere to strict guidelines to minimize potential environmental damage. Different states have enacted their regulations, and the EPA has enacted several regulations that all operations must comply with.
Operators must monitor the water quality of their operations, and if there is any evidence of contamination, they must take action to rectify the situation.
In addition, the EPA requires operators to submit detailed reports about the chemicals used in their operations and detailed monitoring data on the water quality. This data helps the EPA and other government agencies to ensure that all operations are conducted safely and that any potential contamination is addressed quickly and effectively.
Final Thoughts
As we have seen, the effects of fracking on water quality are far-reaching and can be both immediate and long-term. The process of hydraulic fracturing, while providing an important source of energy, has caused significant environmental damage due to the release of hazardous chemicals, the depletion of water resources, and the potential for contamination of the water table.
As such, fracking operations must be closely monitored and regulated to minimize the potential impacts on water quality. It is also essential that environmental organizations and local communities are made aware of the risks associated with fracking and are allowed to voice their concerns. With increased regulation and monitoring, the potential effects of fracking on water quality can be reduced, thus making it a sustainable and reliable energy source.

Jay
Jay is a health and wellness enthusiast with expertise in water quality and nutrition. As a knowledgeable advocate for holistic well-being, Jay successfully manages Type 2 Diabetes through informed lifestyle choices. Committed to sharing reliable and authoritative insights, Jay combines firsthand experience with a passion for enhancing health."

