Drinking safe, clean, and good-tasting water is healthy. In most homes, water purifiers are used to remove bad odors, lead, and other chemical impurities found in water. Water filters have high efficiency, depending on the model acquired.
Different brands and models function in unique ways. If you are planning to buy a water filtration system, here is what to check out;

What water purification is a necessity?
Some water sources are treated for impurities and contaminants that affect water safety. When water passes through worn-out vessels, it gets contaminated again and thus may not be safe for drinking. Water filtration helps in the removal of harmful bacteria and other contaminants.
What you need to know about buying a water filter
Water filters vary in their functions, qualities, and designs. Here are essential facts about water filters you need to know;
- Filter quality: quality differs for different brands, and they remove different types of contaminants at varying efficiency percentages.
- Certification: Just because a filter is NSF Certified does mean it removes a particular contaminant
- The technology used: Some filters use multiple technologies, while others use one to remove contaminants.
Water filtration methods
Before purchasing any model for your home, it is crucial to understand all processes involved in water purification. Some methods are more efficient in removing contaminants than others. For instance, a jug and a water cooler function differently. Here is a look at some filtration mechanisms;
Activated carbon

Activated carbon is sold as granules or solid blocks. Carbon removes contaminants through chemical bonding. It efficiently removes Chlorine, which improves water’s taste, while some will remove Chlorine and lead.
Notably, carbon does not filter inorganic pollutants such as fluorides, nitrates, and arsenic. You will need a different filter if your water source is contaminated with these elements.
Distillation

The method involves heating water until it vaporizes. The vapor is channeled to a condenser, which is reversed back to liquid. The process works great since water has a lower boiling point than most pollutants and microorganisms. The method removes bacteria, sediments, germs, salts, and heavy metals (lead, arsenic, and mercury).
Merit
- It is very effective and cheap in purifying small amounts of water.
Demerits:
- Very costly to purify huge amounts of water (it needs a lot of fuel to boil
- It is slow when purifying huge quantities of water.
Deionization
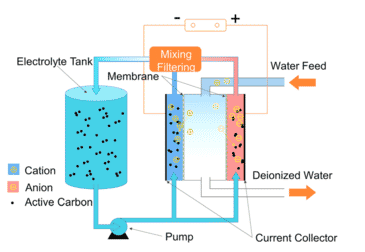
image source by Wikipedia
Deionization uses an exchange of ions in water to remove salts and other electrically charged ions in water. The filter removes elements that lack electric charges. This process does not remove bacteria and viruses.
Chlorination
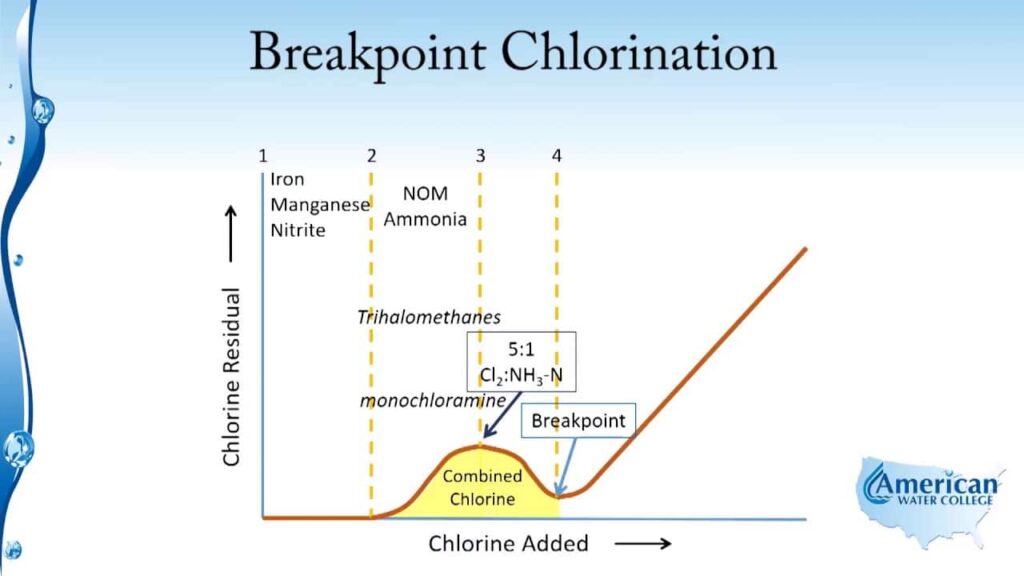
Image source by American Water College
Chlorine is a chemical that kills bacteria, parasites, and other disease-causing microorganisms in water. It is available as tablets or liquid Chlorine at very low prices. Chlorine tablets are dissolved at 12 degrees Celsius or higher. After using Chlorine, reverse osmosis can remove other contaminants in water for higher purity levels.
When using Chlorine, people with thyroid problems need to talk to a medical practitioner before using the water.
Filtration
Filtration through different multimedia filters is a common practice in water purification. The method involves a chemical and physical process to eliminate pollutants and contaminants in water, making it safe for drinking.
Small and large particles are removed through filtration. Since some chemicals are dissolved in water, it is useful for other procedures to be used. The chemical absorption processes remove unwanted compounds from water.
Filtration is preferred to RO when it comes to removing pesticides and Chlorine. Less water is lost during his process, and it does not require a lot of energy. Filtration is also very cheap.
Ion exchange
The ion exchange technology uses resin to replace harmful ions with some which are less dangerous. The method is commonly used for water softening, replacing sodium, calcium, and magnesium with harmless ions.
Reverse osmosis
The reverse osmosis method (RO) is widely used in removing salts, impurities, and germs in the water. In this process, a semi-permeable membrane removes all impurities dissolved in water. The membrane has very tiny pores (0.0005 microns), which are slightly larger than the size of a water molecule.
The shortcoming of this method is that it removes some essential minerals from water, thus altering its taste. Regular maintenance and replacement of the membrane could also be costly.
How the RO water purifiers work will give you a clear picture of how it functions. Larger molecules like those of Chlorine are not removed in the process. The reverse osmosis system is efficient compared to carbon filters, making it a perfect domestic choice.
Mechanical
Mechanical filters remove larger pollutant particles. They cannot remove chemicals dissolved in water. They are handy with other filtration methods where the water is very dirty, and you must get rid of solid waste first.
Ultra-Filtration (UF) purification
UF (Ultra ) works through a membrane similar to RO, but the membrane has bigger pores. The membrane removes colloidal particles such as pathogenic organisms and turbidity.
The membrane fails to remove salts and dissolved solids. UF removes bacteria, microorganisms, and viruses from your water. The water obtained after this process has less TDS and is not very hard. With RO, the water has too many TDS and is very hard.
Ozone
Ozone filters kill microorganisms in water but do not remove chemicals. They are used alongside other technologies for high efficiency.
Carbon block
The carbon filters have crushed carbon particles, which makes them more efficient than other carbon filters. The increased surface area gives them a higher sediment-holding capacity than most filters. It has activated carbon, which has millions of pores that absorbs substances from liquids.
Activated carbon has a larger surface area for bonding chemicals, trapping carbon-based impurities and Chlorine. Sodium and nitrates pass through the filter. The carbon block filter must be replaced for efficiency when the pores are clogged and stop working.
Granulated carbon
The filters use small particles of carbon to remove impurities in water. They have a smaller surface area, which lowers their efficiency compared to other block-shaped filters. Their filtration speed depends on water speed.
UV Purification or E-boiling
UV water purification uses ultraviolet light to kill germs, bacteria, cysts, and other microbes found in water. It destroys about 99.99% of microorganisms in water. The cleaner is built with a mercury lamp that produces UV radiations that destroy all microorganisms.
While the microbes are killed, their bodies remain in the water. A separate filtration system is used to get rid of germs physically. Carbon filters or reverse osmosis may come in handy in producing more purified water.
Water softeners
Water softeners use ion exchange technology to remove magnesium and calcium ions from water. The process involves using sodium in the softening process. The resulting water will have higher levels of sodium. If you do not need a lot of salt in your water, avoiding water softeners in your plumbing systems is useful. Water with high salt is also not suitable for watering plants.
Candle filter purifier
The candle filter has toney pores that block larger particles. The candle does not need electricity to function. The candle needs to be cleaned frequently to unblock the pores for greater results. Water resulting from this process must be boiled to kill microbes.
Boiling
Boiling water is the cheapest method of purification. Water may contain some bacteria and life-threatening germs that are invisible. Boiling water for 1-3 minutes kills most microorganisms in water. The boiled water is left to cool down before drinking. If you live in high-altitude areas, allow water to boil longer since the boiling point is slightly lower.
Fiber filters
These filters contain rayon, cellulose, and other materials designed into a mesh with tiny pores. Water is poured over the filter, and it passes through the pores. For this method, some pressure is applied to force water through the tiny wrapped filters. Check for a micron rating below 1 for high efficiency when buying a good filter.
Types of water filters
Here are the best types of water filters;
Pitchers
They contain carbon filters that improve water taste and odor by removing contaminants.
They are affordable and can fit in most refrigerators
Read our article for the best water filter pitchers.
Under-sink
Installed under the sink and attached to your water line.
Slightly expensive but need proper maintenance for longer performance
Here are a few of the best under sink water filters.
On-counter
Used on the counter and fitted directly on the faucet.
Have a switch to move from filtered to unfiltered water. The countertop water coolers are easy to use and need little effort.
Making the right decision
The number of filtration systems in the market is overwhelming. You must make the correct decision regarding your home water usage and needs. Keep your personal needs in mind when picking a suitable model.
The other crucial thing is understanding how a filter system works. Go for something simple and efficient.
Installing a perfect water filter in your home will ensure constant access to clean and healthy water.

Jay
Jay is a health and wellness enthusiast with expertise in water quality and nutrition. As a knowledgeable advocate for holistic well-being, Jay successfully manages Type 2 Diabetes through informed lifestyle choices. Committed to sharing reliable and authoritative insights, Jay combines firsthand experience with a passion for enhancing health."
